Forecast Methods and Models

Hurricane forecast – Meteorologists use a variety of methods and models to forecast hurricanes. These methods range from simple statistical techniques to complex computer simulations. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and meteorologists often use a combination of methods to get the most accurate forecast.
Statistical Methods
Statistical methods are based on the assumption that past hurricane behavior can be used to predict future behavior. These methods use historical data on hurricane tracks, intensities, and other factors to develop statistical models that can be used to forecast future hurricanes.
Statistical methods are relatively simple and inexpensive to use, and they can be used to make forecasts for a wide range of lead times. However, statistical methods are limited by the assumption that past behavior will continue into the future. This assumption can be violated by changes in climate or other factors.
Dynamical Models
Dynamical models are based on the laws of physics that govern the atmosphere and oceans. These models use mathematical equations to simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and oceans, and they can be used to forecast hurricanes by simulating their evolution over time.
Dynamical models are more complex and expensive to use than statistical methods, and they can only be used to make forecasts for relatively short lead times. However, dynamical models are more accurate than statistical methods, and they can provide more detailed information about the forecast hurricane.
Ensemble Forecasting
Ensemble forecasting is a technique that uses multiple dynamical models to make a forecast. This technique involves running a series of dynamical models with slightly different initial conditions. The results of the individual models are then combined to produce a forecast that is more accurate than any of the individual models.
Ensemble forecasting is a relatively new technique, but it has shown promise for improving the accuracy of hurricane forecasts. This technique is likely to become more widely used in the future.
Factors Influencing Hurricane Formation and Intensity
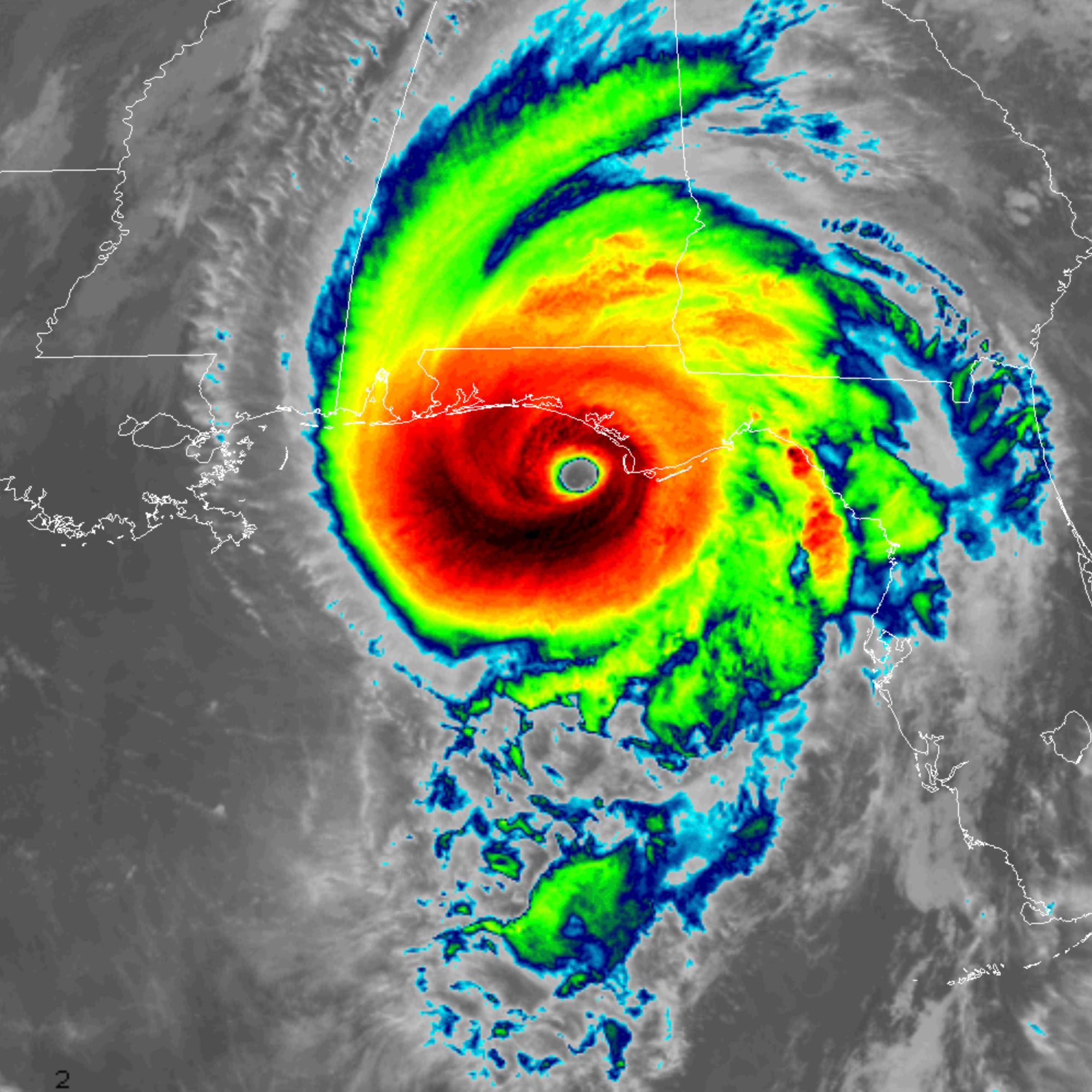
The formation and intensity of hurricanes are influenced by a complex interplay of atmospheric and oceanic factors. These factors interact to create the conditions necessary for hurricane development, and they can also influence the severity and path of the storm.
Sea Surface Temperatures
Warm ocean waters provide the energy that fuels hurricanes. The temperature of the sea surface must be at least 26.5 degrees Celsius (79.7 degrees Fahrenheit) for a hurricane to form. This warm water provides the moisture and energy that the storm needs to grow and intensify.
Atmospheric Pressure
Hurricanes form in areas of low atmospheric pressure. When the pressure difference between the ocean surface and the upper atmosphere is large, it creates a pressure gradient that drives the winds. The stronger the pressure gradient, the stronger the winds will be.
Vertical Wind Shear
Vertical wind shear is the difference in wind speed and direction between different levels of the atmosphere. High vertical wind shear can disrupt the development of hurricanes by preventing the storm from organizing and intensifying.
Coriolis Effect
The Coriolis effect is a force that deflects objects moving in the atmosphere or ocean to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. The Coriolis effect helps to give hurricanes their characteristic counterclockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere.
Historical Examples, Hurricane forecast
These factors have played a role in the development of many historical hurricanes. For example, the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico contributed to the intensity of Hurricane Katrina in 2005. The low atmospheric pressure and high vertical wind shear in the Caribbean Sea helped to weaken Hurricane Irma in 2017. And the Coriolis effect caused Hurricane Sandy to make a sharp turn to the west in 2012, sparing the New England coast from a direct hit.
Data Analysis and Visualization: Hurricane Forecast

Data analysis and visualization play a crucial role in hurricane forecasting by providing valuable insights into hurricane behavior and enabling meteorologists to make more accurate predictions.
Types of Data Used for Hurricane Forecasting
- Historical hurricane data: Includes information on past hurricanes, such as their tracks, intensities, and landfall locations.
- Real-time observations: Data collected from weather stations, buoys, satellites, and aircraft, providing information on current atmospheric conditions and hurricane characteristics.
- Model simulations: Output from numerical weather prediction models, which simulate the behavior of the atmosphere and oceans to predict hurricane formation, movement, and intensity.
Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis techniques are used to identify patterns and trends in hurricane behavior, including:
- Statistical analysis: Used to identify correlations between hurricane characteristics and atmospheric conditions.
- Machine learning: Algorithms are trained on historical data to predict hurricane behavior based on current conditions.
- Ensemble forecasting: Combining multiple model simulations to generate a more accurate forecast.
Interactive Visualization
Interactive visualizations can help meteorologists and the public understand hurricane behavior and forecast accuracy. For example, a visualization could show:
- Historical hurricane tracks overlaid on real-time observations.
- Ensemble forecast tracks, indicating the range of possible hurricane paths.
- A map of hurricane intensity probabilities.
By visualizing data, meteorologists can quickly identify patterns and trends, improve forecast accuracy, and communicate hurricane risks more effectively to the public.